Volume 2, Issue 1, January-February 2021.
X-Ray Testing
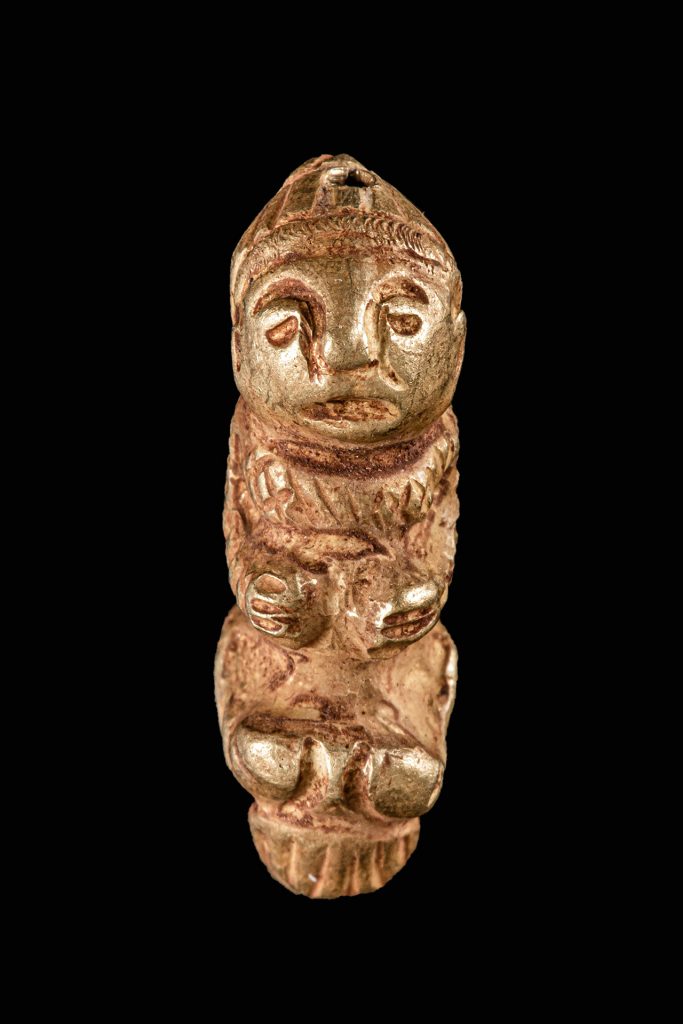
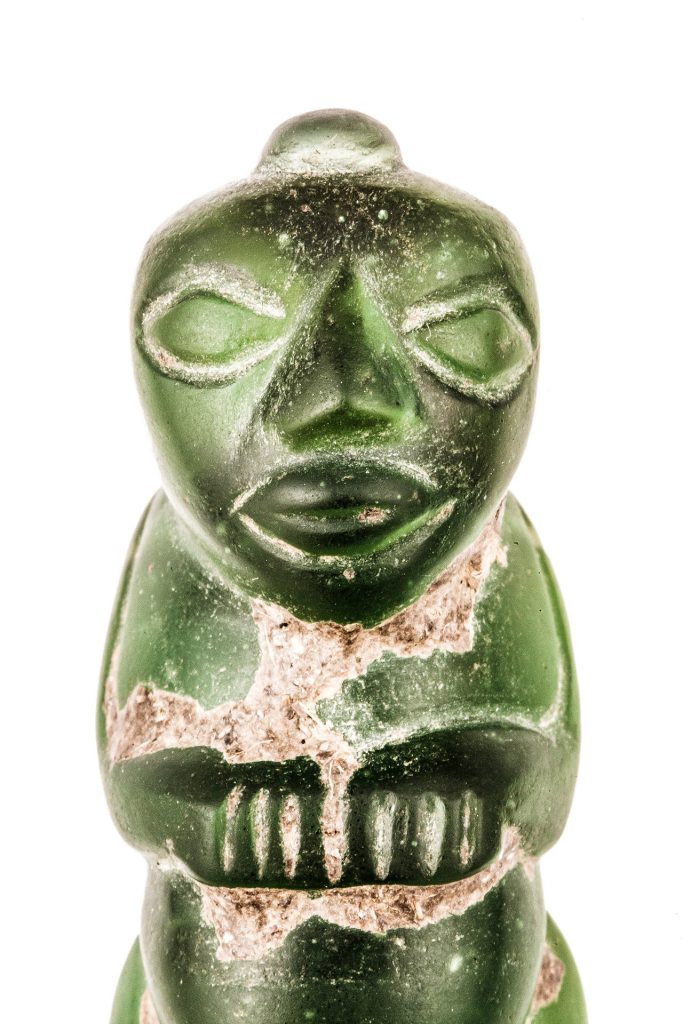
Results for the burmese gold beads
by Dr. Judith Horváth
Precise measuring method for gold based jewellery alloys
ABSTRACT
In most countries around the world, the quality of objects made from precious metals has always been regulated by law and regulation since time immemorial. Analytical precision and the speed of analysis are both very important. Currently, there are several methods we know of to determine gold, but it is difficult to achieve precision without simultaneous destruction because the prescribed level of accuracy is very strict. When testing gold jewellery alloys we selected the X-ray testing method. We have tested every piece presented in this book and we have issued official certificates for each measurement. The results are summarised in a table below.
Introduction
Precious metals have always been considered to be special alloys because of their value and their rarity. Nowadays, in most counties the quality of objects made from precious metals is regulated by law. In these countries there are assay offices supported by accredited laboratories that are able to analyse all kinds of jewellery alloys. In addition to analytical precision the speed of analysis is also very important. In Hungary precious metal analyses and hallmarking are supervised by the Ministry of National Economy. Analyses, hallmarking and checks are carried out by the Hungarian Trade Licencing Office, which is a member of the International Association of Assay Offices. Currently the law regarding precious metals prescribes that every object made from gold, silver, platinum and palladium must have the quality prescribed by law.
During the testing of jewellery alloys containing gold, non-destructive determination is sometimes an indispensable demand. This prerequisite is present in the jewellery industry or in archaeology and sometimes in the procedures of authorities.
We currently know of several ways of determining gold, but it is difficult to achieve precision without simultaneously causing destruction because the prescribed level of accuracy is very strict. When testing gold jewellery alloys we chose the X-Ray testing method.
The aim of our research is to find a gold measuring method that is non-destructive and accurate that can substitute the touchstone test, has low operating costs and at the same time is able to take everyday practice and international standard regulations into account.

Dr. Judith Horváth
Former Head of the Laboratory at the Hungarian Trade Licencing Office
– Assay Authority (Budapest)
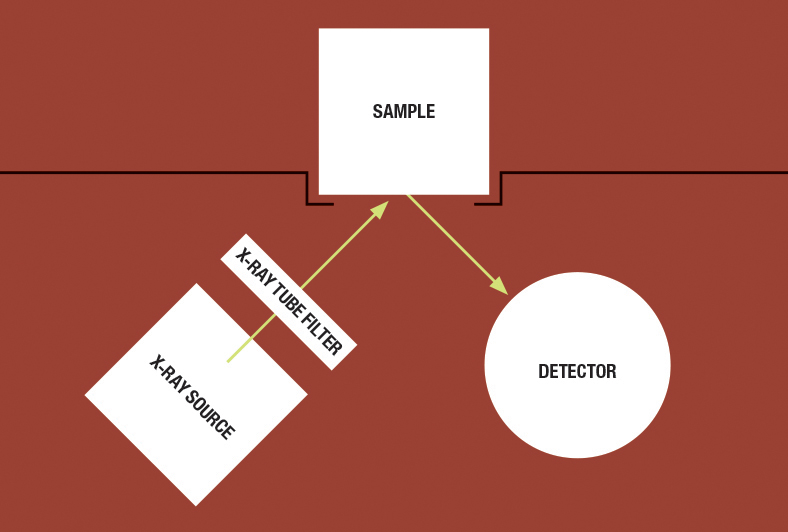
The summary of performed research and analyses
At the outset of our research we studied the touchstone test, the fire assay method, the ICP and other spectrometic methods. For testing gold jewellery alloys we chose the X-Ray testing method.
Nowadays, spectrometric based measuring methods are increasingly common and this technology is gaining greater importance in precious metal analysis. The principle of the X-Ray spectrometric measuring method is that we use X-rays to excite the elements of the material being tested, causing them to emit fluorescent radiation. Measuring the energy and intensity of these emissions allows the elements to be identified and quantified.
The X-Ray method has many advantages over the fire assay method:
– It is non-destructive and we can analyse objects without damage
– All elements in the alloys can be determined simultaneously
– The method is computerized, which means that time and cost can be reduced
– Environmental hazards are not an issue
The disadvantages of the method are the following:
– It is matrix-dependent, so if the homogeneity is problematic then not only the surface but also the cross-section has to be measured.
The X-Ray measuring method is precise to 0.5% for gold, silver and platinum, and 1% for other elements like Rh, Ir, Pd, Cu, Zn, Fe, Cr, Ni, Co, Cd, Sn, Pb, Mo, and W. Jewellerymaking specialists and analysts consider this method to be the solution to several problems in the area.
We performed the tests using a Midex M X-ray machine. The sample range of this device suits it to the inspection of larger objects, archaeological finds and works of art. The sample holder is not adjusted manually, but rather by a motorised, computer-controlled bench that can move along the x, y and z axes so manual adjustment of the objects is rarely required. The X-rays can be focussed onto a single point, which allows locations that are difficult to reach to be tested. In addition, every single measurement is saved, which subsequently allows complete documentation to be prepared.
We have tested each item in the Zelnik Collection individually. Objects consisting of several parts were tested piece by piece. We issued individual official certificates for each examination. We have also summarised the measurement results in a separate table.


